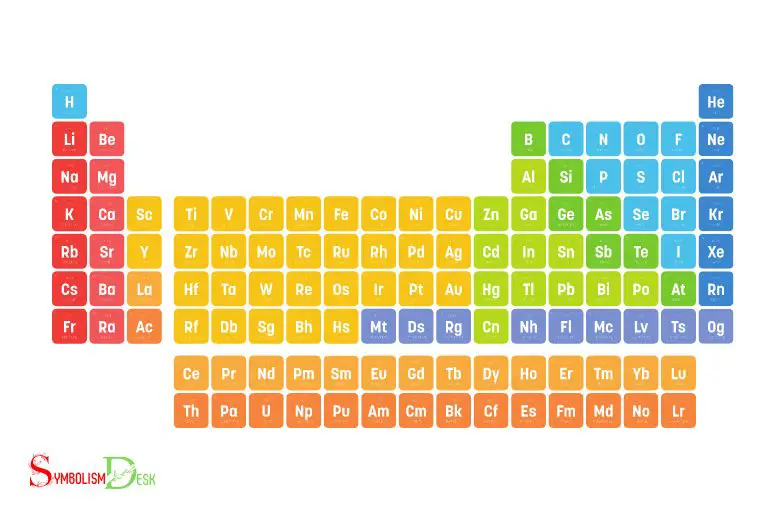
Periodic Table of Elements With Symbols And Names
The periodic table of elements with symbols and names is a tabular arrangement of all known chemical elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties.
The periodic table was first introduced by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. It helps scientists understand the relationships between elements and predict their chemical behavior.
Elements in the periodic table are arranged in rows called periods and columns called groups. Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties.
The periodic table of elements serves as a fundamental tool for chemists and other scientists, allowing them to quickly identify an element’s symbol, atomic number, and atomic mass.
Additionally, it helps in understanding the chemical reactivity and trends in properties of elements, such as ionization energy, electronegativity, and atomic radius.
118 Periodic Table of Elements With Symbols
| Element | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H |
| Helium | He |
| Lithium | Li |
| Beryllium | Be |
| Boron | B |
| Carbon | C |
| Nitrogen | N |
| Oxygen | O |
| Fluorine | F |
| Neon | Ne |
| Sodium | Na |
| Magnesium | Mg |
| Aluminum | Al |
| Silicon | Si |
| Phosphorus | P |
| Sulfur | S |
| Chlorine | Cl |
| Argon | Ar |
| Potassium | K |
| Calcium | Ca |
| Scandium | Sc |
| Titanium | Ti |
| Vanadium | V |
| Chromium | Cr |
| Manganese | Mn |
| Iron | Fe |
| Cobalt | Co |
| Nickel | Ni |
| Copper | Cu |
| Zinc | Zn |
| Gallium | Ga |
| Germanium | Ge |
| Arsenic | As |
| Selenium | Se |
| Bromine | Br |
| Krypton | Kr |
| Rubidium | Rb |
| Strontium | Sr |
| Yttrium | Y |
| Zirconium | Zr |
| Niobium | Nb |
| Molybdenum | Mo |
| Technetium | Tc |
| Ruthenium | Ru |
| Rhodium | Rh |
| Palladium | Pd |
| Silver | Ag |
| Cadmium | Cd |
| Indium | In |
| Tin | Sn |
| Antimony | Sb |
| Tellurium | Te |
| Iodine | I |
| Xenon | Xe |
| Cesium | Cs |
| Barium | Ba |
| Lanthanum | La |
| Cerium | Ce |
| Praseodymium | Pr |
| Neodymium | Nd |
| Promethium | Pm |
| Samarium | Sm |
| Europium | Eu |
| Gadolinium | Gd |
| Terbium | Tb |
| Dysprosium | Dy |
| Holmium | Ho |
| Erbium | Er |
| Thulium | Tm |
| Ytterbium | Yb |
| Lutetium | Lu |
| Hafnium | Hf |
| Tantalum | Ta |
| Tungsten | W |
| Rhenium | Re |
| Osmium | Os |
| Iridium | Ir |
| Platinum | Pt |
| Gold | Au |
| Mercury | Hg |
| Thallium | Tl |
| Lead | Pb |
| Bismuth | Bi |
| Polonium | Po |
| Astatine | At |
| Radon | Rn |
| Francium | Fr |
| Radium | Ra |
| Actinium | Ac |
| Thorium | Th |
| Protactinium | Pa |
| Uranium | U |
| Neptunium | Np |
| Plutonium | Pu |
| Americium | Am |
| Curium | Cm |
| Berkelium | Bk |
| Californium | Cf |
| Einsteinium | Es |
| Fermium | Fm |
| Mendelevium | Md |
| Nobelium | No |
| Lawrencium | Lr |
| Rutherfordium | Rf |
| Dubnium | Db |
| Seaborgium | Sg |
| Bohrium | Bh |
| Hassium | Hs |
| Meitnerium | Mt |
| Darmstadtium | Ds |
| Roentgenium | Rg |
| Copernicium | Cn |
| Nihonium | Nh |
| Flerovium | Fl |
| Moscovium | Mc |
| Livermorium | Lv |
| Tennessine | Ts |
| Oganesson | Og |
Key Takeaway
Five Facts About Periodic Table Of Elements
Introduction: Understanding The Periodic Table
The Significance Of The Periodic Table In Chemistry And Science
The periodic table is a critical tool for understanding the building blocks of our universe. It organizes 118 known elements into rows and columns according to their atomic number, electron configuration, and chemical properties.
Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- The periodic table helps chemists predict how elements will react with one another and determine their specific properties.
- Scientists use the periodic table to identify and classify newly discovered elements in the laboratory.
- The periodic table is fundamental to understanding chemical reactions and the basic principles of chemistry.
Brief History Of The Periodic Table
The periodic table has a fascinating and complex history, which dates back to the ancient greeks who first observed the existence of elements.
Here are some key points to understand:
- The modern periodic table was developed by a russian chemist named dmitri mendeleev in 1869, who organized the elements by properties and predicted the discovery of new elements.
- Over time, new discoveries and scientific advancements have led to the refinement of the periodic table. For instance, the discovery of subatomic particles has allowed scientists to better understand the properties of elements and how they interact with one another.
- The periodic table has applications beyond the field of chemistry. For instance, it is used by geologists to understand the behavior of elements and minerals in the earth’s crust.
Knowing the significance of the periodic table in chemistry and science, as well as the history behind its creation, is essential for anyone studying chemistry or science.
The periodic table offers insight into the building blocks of our universe and allows scientists to make predictions and discoveries that have far-reaching implications.
Structure Of The Periodic Table
The Basic Structure Of The Periodic Table
The periodic table is a system of organizing the known elements in a specified format. Each element is represented by a unique symbol and name, arranged in ascending order based on their atomic number.
The periodic table is a rectangular-shaped table, consisting of horizontal rows (periods) and vertical columns (groups/families), that are numbered from 1 to 18.
Understanding The Rows (Periods) And Columns (Groups/Families)
The vertical columns in the periodic table are known as groups or families, and each group contains elements with similar characteristics.
The elements in a group have the same number of valence electrons in their outermost shell and exhibit similar chemical behaviors.
For instance, elements in group 1 are known as alkali metals, which are highly reactive, while elements in group 18 are called noble gases, which are known to be chemically unreactive.
The horizontal rows in the periodic table are known as periods. A period corresponds to the energy level or electron shell of the elements within it. Each successive period corresponds to a new energy level or shell that is filled with electrons.
The first period has only two elements, namely hydrogen and helium, while the second period has eight elements, and so on.
Key Features Of The Periodic Table
The periodic table is designed to make it easy to predict the properties of an element based on its location within the table.
Here are some key features of the periodic table:
- Each element has a unique symbol and name, which are used to represent it. The symbol is usually an abbreviation of the element name.
- The elements are arranged in ascending order based on their atomic number. This means that elements with similar properties are grouped together.
- The elements are classified into metals, nonmetals, and metalloids or semimetals based on their physical and chemical properties. Metals are generally found on the left side of the periodic table, while nonmetals are found on the right side.
- The periodic table helps to predict the reactivity of an element based on its location in the table. Reactive elements are usually located on the left side of the table, while non-reactive elements are found on the right side.
- The periodic table also helps to predict the size of an atom based on its location within the table. Atoms generally get larger as you move down the table and smaller as you move from left to right.
These key features make the periodic table a powerful tool for understanding the properties and behaviors of the elements that make up our world.
Elements, Symbols, And Names
Overview Of Elements And Their Properties
The periodic table of elements categorizes all known elements in a specific order based on their chemical and physical properties.
This table lists a total of 118 elements, presenting them in rows and columns that are based on their atomic weight, electron configuration, and chemical behavior.
The elements are broken down into three main groups: metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. While each element possesses unique properties, their placement on the table helps scientists understand the elements’ behavior and properties.
The Use Of Symbols And Names In The Periodic Table
Every element in the periodic table has a unique symbol and name that are used to identify it. Most of the symbols in the table are derived from the element’s name, which can be one, two, or three letters long.
For example, helium has the symbol he, and carbon has the symbol c. the unique names assigned to each element in the table are essential for identifying them, particularly within the context of chemical reactions and experiments.
By using symbols and names, scientists can easily communicate precise information about the element and its properties.
How Elements Are Classified In The Periodic Table
The elements in the periodic table are classified into groups based on their electron configuration.
These groups are known as periods and columns, and each has a specific set of chemical and physical properties that define it. There are seven horizontal rows in the table, and they are called periods.
The elements in each period follow a pattern where the first element has one electron in its outer shell, and the last element in a period has a completely full outer shell. The elements are further classified into 18 vertical columns known as groups.
Each group in the table has a unique set of properties, such as reactivity, ionization energy, and electronegativity. Understanding how elements are classified in the table enables chemists to predict their behavior and interactions with other elements.
Groups And Families
Overview Of Groups And Families In The Periodic Table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of all known chemical elements in such a way that their properties can be observed and compared.
It has been divided into groups and families based on the elements’ electronic configurations and chemical properties.
Below are the key takeaways about groups and families:
- Groups are vertical columns in the periodic table and include elements having the same number of valence electrons.
- Families are horizontal rows in the periodic table and have similar physical and chemical properties.
- The groups are numbered from 1 to 18, and each group has a specific name based on its properties.
The Properties Of Elements Within Each Group And Family
The elements in each group and family of the periodic table have distinct features.
Here are some of the properties:
- Alkali metals are found in the first group of the periodic table and are the most reactive metals. They have only one valence electron and form ionic bonds easily.
- Halogens are non-metals found in group 17 of the periodic table. They have 7 valence electrons and are highly reactive when it comes to forming compounds.
- Noble gases are the most inert and stable elements in the periodic table, found in group 18. They have a complete outer shell, making them resistant to chemical reactions.
- Transition metals are found in groups 3 to 12 and exhibit characteristics of both metals and nonmetals. They have various oxidation states and form brightly colored compounds.
- Lanthanides and actinides are found at the bottom of the periodic table and are often called inner transition metals. They include elements with atomic numbers 57 to 71 and 89 to 103, respectively.
Key Differences Between Groups And Families
Although groups and families have similar properties, there are also key differences between them.
Here are some of the differences:
- Groups are vertical columns, while families are horizontal rows.
- Groups are identified by numbers 1-18, while families have specific names that often indicate similar properties.
- Elements in the same family have similar chemical properties, while elements in a group have the same number of valence electrons.
- The elements in each group have different numbers of energy shells with an increasing number of electrons.
Understanding the periodic table’s basic structure and identifying the elements’ properties in each group and family can help us predict how they will react and form chemical compounds.
Knowing the differences between groups and families is also essential for accurately identifying and classifying elements.
Applications Of The Periodic Table
Periodic Table Of Elements With Symbols And Names
The periodic table is one of the essential tools in chemistry, listing all the known chemical elements in order of atomic number.
Without it, scientists would find it challenging to explain the variety of chemical reactions and materials in the universe.
We will explore the practical applications, how it has contributed to the advancements in science and technology, and its future implications.
Practical Applications Of The Periodic Table
The periodic table is not just a tool for chemistry teachers or scientists, but it touches almost all aspects of our lives.
Below are some of the practical applications of the periodic table:
- Medicine: The table helps chemists in designing drugs and researching elements that can be used to fight diseases.
- Agriculture: The table helps to identify the necessary minerals and elements for growing plants and improving soil quality.
- Technology: Elements on the periodic table are used in a wide range of technologies, including electronics, aerospace, and construction.
- Environmental studies: Chemists can use the table to study the effects of pollution and the movement of chemicals in the environment.
How The Periodic Table Has Contributed To Developments In Science And Technology
The periodic table has played a significant role in shaping the developments in science and technology.
Here are some ways the periodic table has contributed:
- Prediction of new elements: Using the periodic table, scientists were able to predict the properties of the unknown elements and even their atomic masses.
- Development of new technologies: Scientists have used the periodic table to create new materials with unique properties that have been used to develop different technologies.
- Understanding the bonding of atoms: Scientists have used the periodic table to understand how atoms bond with each other, which has led to breakthroughs in material science and nanotechnology.
Future Implications Of The Periodic Table
The periodic table will continue to play a crucial role in the future of science and technology.
Here are some future implications:
- Development of new materials: The periodic table could be used to develop new materials with unique properties that could be used in different fields such as electronics, medicine, and construction.
- Advancements in nanotechnology: With a better understanding of the bonding of atoms, scientists can discover new applications in nanotechnology.
- Discovering new elements: There are still unknown elements beyond the current periodic table that could be discovered shortly, leading to new discoveries and developments.
The periodic table remains one of the essential tools in chemistry with far-reaching practical applications and future implications that will shape science and technology.
Why Don’t the Symbols of These Elements Match Their Names?
Why are there symbols with names that don’t match? It’s a curious phenomenon found in the periodic table. For example, the symbol for gold is Au instead of Go, and potassium is represented by K rather than Po. This mismatch between symbols and names can be attributed to historical reasons, language abbreviations, or even the use of Latin words. Nevertheless, it adds an intriguing layer to the study of elements.
FAQ On Periodic Table Of Elements With Symbols And Names
What Is The Periodic Table Of Elements?
The periodic table is a table of the chemical elements arranged based on their atomic number and chemical properties.
How Many Elements Are There In The Periodic Table?
The periodic table currently has 118 known elements, including both naturally occurring and man-made elements.
What Are The Symbols Used In The Periodic Table?
Symbols are abbreviated forms of the element names used in the periodic table. For example, h is the symbol for hydrogen.
How Are Elements Arranged In The Periodic Table?
Elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, from left to right and top to bottom, grouped by similar properties.
Why Is The Periodic Table Important?
The periodic table is important because it provides scientists with a systematic way to organize and study the elements and their properties. It is also used extensively in chemistry and other sciences.
Conclusion
We have explored the iconic periodic table of elements with symbols and names in this blog post. It’s fascinating to learn about the building blocks of our world and how they interact with each other. Understanding the table makes chemistry much more accessible and enjoyable.
While the table has evolved since its inception, it remains an essential tool for chemists, students, and scientists worldwide.
The elements we discussed have unique properties and uses, highlighting their importance in our daily lives. From the crucial role of oxygen in our breathing to the uses of gold and silver in jewelry, it’s clear that elements impact our daily lives.
Overall, the periodic table will always be a fundamental aspect of chemistry, guiding us on our journey towards understanding the world around us.
Professionals and students alike will continue to reference it for many years to come, and its value cannot be overstated.







