What Do the Symbols Mean in the Periodic Table? Elements!
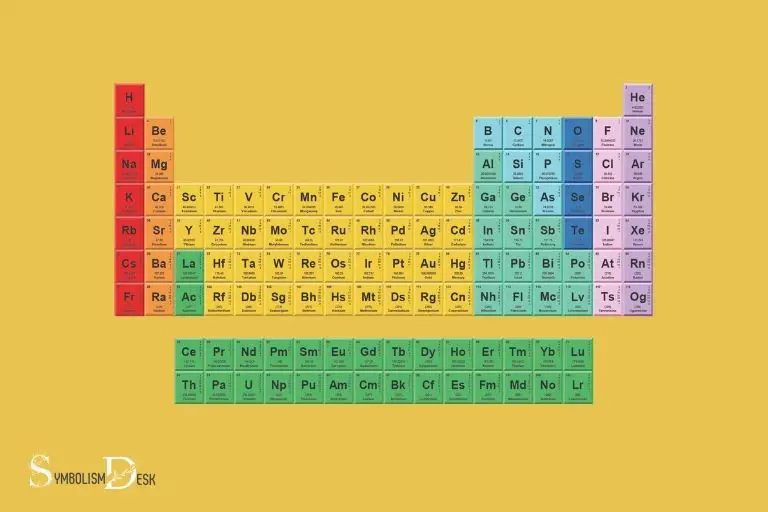
The symbols in the periodic table represent the different elements. Each symbol consists of one or two letters that are derived from the element’s name in English, Latin, or other languages.
For instance, the symbol ‘H’ denotes Hydrogen, while ‘Au’ represents Gold, deriving from its Latin name ‘Aurum’.
The periodic table of elements is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, ordered based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
The symbols are a standardized set of abbreviations for the elements and are universally accepted.
The periodic table’s symbols are an essential part of chemistry, enabling scientists to easily identify and work with different elements.
They serve as a universal language, ensuring that scientists across the globe can understand and communicate chemical information effectively.
The symbols, combined with the structured layout of the periodic table, provide a comprehensive snapshot of each element’s characteristics and behaviors.
88 Symbols and Meanings in the Periodic Table
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| H | Hydrogen |
| He | Helium |
| Li | Lithium |
| Be | Beryllium |
| B | Boron |
| C | Carbon |
| N | Nitrogen |
| O | Oxygen |
| F | Fluorine |
| Ne | Neon |
| Na | Sodium |
| Mg | Magnesium |
| Al | Aluminium |
| Si | Silicon |
| P | Phosphorus |
| S | Sulfur |
| Cl | Chlorine |
| Ar | Argon |
| K | Potassium |
| Ca | Calcium |
| Sc | Scandium |
| Ti | Titanium |
| V | Vanadium |
| Cr | Chromium |
| Mn | Manganese |
| Fe | Iron |
| Co | Cobalt |
| Ni | Nickel |
| Cu | Copper |
| Zn | Zinc |
| Ga | Gallium |
| Ge | Germanium |
| As | Arsenic |
| Se | Selenium |
| Br | Bromine |
| Kr | Krypton |
| Rb | Rubidium |
| Sr | Strontium |
| Y | Yttrium |
| Zr | Zirconium |
| Nb | Niobium |
| Mo | Molybdenum |
| Tc | Technetium |
| Ru | Ruthenium |
| Rh | Rhodium |
| Pd | Palladium |
| Ag | Silver |
| Cd | Cadmium |
| In | Indium |
| Sn | Tin |
| Sb | Antimony |
| Te | Tellurium |
| I | Iodine |
| Xe | Xenon |
| Cs | Cesium |
| Ba | Barium |
| La | Lanthanum |
| Ce | Cerium |
| Pr | Praseodymium |
| Nd | Neodymium |
| Pm | Promethium |
| Sm | Samarium |
| Eu | Europium |
| Gd | Gadolinium |
| Tb | Terbium |
| Dy | Dysprosium |
| Ho | Holmium |
| Er | Erbium |
| Tm | Thulium |
| Yb | Ytterbium |
| Lu | Lutetium |
| Hf | Hafnium |
| Ta | Tantalum |
| W | Tungsten |
| Re | Rhenium |
| Os | Osmium |
| Ir | Iridium |
| Pt | Platinum |
| Au | Gold |
| Hg | Mercury |
| Tl | Thallium |
| Pb | Lead |
| Bi | Bismuth |
| Th | Thorium |
| Pa | Protactinium |
| U | Uranium |
| Np | Neptunium |
| Pu | Plutonium |
Key Takeaway
Five Facts About: The Elements on the Periodic Table
What Are Periodic Table Symbols?
The periodic table – a familiar sight to anyone who has studied chemistry or atomic science – contains a wealth of information about the elements that make up our world.
But, to the uninitiated, the symbols and abbreviations listed on the table can be challenging to interpret.
We will focus on the meaning of the periodic table symbols, explaining their definitions and key points.
Definition Of Periodic Table Symbols
At its essence, the periodic table is a way of representing the chemical elements, and their atomic structures and properties, in a systematic and organized manner.
The table contains 118 known elements, each represented by a unique symbol, comprising one to three letters, based on the element’s name (or, in some cases, its latin name or systematic name).
So, let us take a closer look at how these symbols are formed and what they mean.
Group Symbol
Each element on the periodic table appears alongside a one or two-digit number, known as the atomic number.
This number indicates the number of protons in the element’s nucleus and decides the element’s unique chemical properties.
The elements are further arranged into groups, or columns, with similar chemical properties.
These groups are denoted by a numbered column or a unique letter, such as the halogens (group 17) or the noble gases (group 18).
Period Symbol
The periods, or rows, on the periodic table indicate the principal shell or quantum level of electrons around each element’s nucleus.
The row number identifies the element’s highest electron shell, with rows two to seven representing the s, p, d, f, g, and h shells, respectively.
The elements of each period are ordered by atomic number.
Periods also tend to align with the number of occupied energy levels, with each period representing the addition of a new energy level to an atom.
All the elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
Isotope Symbols
Some elements have isotopes – atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes are identified on the periodic table by writing the atomic mass number, a, as a superscript before the element symbol.
The atomic mass number results from the combined number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus.
For example, the element carbon has two stable isotopes – carbon-12 and carbon-14. Carbon-12 has six neutrons, meaning its atomic mass number is 12 and its symbol is written as 12c.
Understanding the periodic table symbols is crucial for scientists and researchers to understand how atoms interact with one another and to create new compounds and products.
The symbols, although seemingly cryptic and complicated, represent a vital reference tool for anyone studying the building blocks of life.
A Brief History Of The Periodic Table
The periodic table is a vital tool in the world of chemistry, acting as a guide for scientists all around the globe to discover and understand new elements.
But how did it come about? In this section, we will take a closer look at the history of the periodic table, and how it evolved into the vital scientific tool we know today.
Introduction To The Periodic Table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of all chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic numbers.
The table includes symbols, atomic numbers, and atomic weights of the elements, as well as a brief description of their properties.
This organization has proven to be an invaluable resource for chemists worldwide throughout the years.
The Evolution Of The Peridic Table
The development of the periodic table was not an overnight success.
A number of scientists and researchers contributed to its development over the years, with each adding their own unique insight into its structure and organization.
Here are some key milestones:
- 1789: Antoine lavoisier creates a list of 33 elements and categorizes them as gases, metals, nonmetals, and earths.
- 1817: Johann döbereiner discovers the law of triads, a set of triads of elements.
- 1862: Alexandre-emile beguyer de chancourtois proposes an early version of the periodic table based on atomic weights.
- 1869: Dmitri ivanovich mendeleev develops the modern periodic table, recognizing patterns in the atomic weights of elements.
- 1913: Henry moseley uses x-rays to measure the atomic numbers of elements, leading to a more accurate periodic table.
The research of these eminent scientists and others helped in the creation of the present-day version of the periodic table which continues to evolve.
The birth and growth of the periodic table is an extraordinary story of scientific progress and unraveling the structure of the universe.
The constant research and discovery to update the periodic table have helped to advance the knowledge of humankind.
The periodic table serves as an essential tool for scientists to identify new elements, predict their behavior and explore their potential applications.
The Structure Of The Periodic Table
Overview Of The Periodic Table Structure
The periodic table is a crucial tool in understanding chemistry. Its structure is designed to illustrate the patterns and characteristics of elements based on their properties.
Here are some key points to help you understand the structure of the periodic table:
- The table is organized into rows called periods and columns called groups.
- The elements are arranged in order of their atomic number, which is the total number of protons in their nucleus.
- The properties of elements repeat in a predictable way from one period to the next.
Groups And Periods In The Periodic Table
The structure of the periodic table is based on elements that share similar properties. These similarities are due to the number of valence electrons, or outermost electrons, an element has in its atom.
Here are some key points to help you understand groups and periods in the periodic table:
- Groups are the vertical columns arranged from left to right on the periodic table.
- Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons, which determines their chemical properties.
- The periodic table is divided into four main blocks: S-block, p-block, d-block and f-block. Each block corresponds to the different elements’ valence electrons.
Here’s a brief overview of each period in the periodic table along with their corresponding subshells:
- Period 1 has only two elements, hydrogen and helium, both of which have only one subshell.
- Period 2 has six elements, lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen, with two subshells.
- Period 3 has eight elements, sodium, magnesium, aluminum, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon, with three subshells.
- Period 4 has 18 elements, starting with potassium and ending with krypton, which have four subshells.
- Period 5 has 18 elements, starting with rubidium and ending with xenon, also with four subshells.
- Period 6 has 18 elements, starting with cesium and ending with radon, with five subshells.
- Period 7 has only 12 elements, with the four heaviest elements currently known: Francium, radium, actinium, and lawrencium.
The structure of the periodic table is based on organizing elements in a way that emphasizes their properties.
The arrangement of elements based on their valence electrons and subshells allow for the prediction of chemical reactions and the creation of new compounds.
Understanding the organization of the periodic table is crucial for anyone studying chemistry.
Understanding The Symbols In The Periodic Table
The Meaning Of Symbols In The Periodic Table
The periodic table is a comprehensive collection of all the chemical elements that exist, arranged in a specific order based on their atomic structure.
A typical periodic table includes various symbols, such as h for hydrogen, he for helium, and li for lithium.
These symbols hold significant importance as they represent the identity of that particular element.
Here are a few key points to understand the meaning of symbols in the periodic table:
- Every element has a unique symbol that is used to represent it.
- The symbol of an element is usually derived from its name, and it is a combination of one or two letters.
- The first letter of the symbol is always capitalized, and in some cases, the second letter may also be capitalized.
- The symbol is a shorthand way of representing an element and is used in equations and formulae where space is limited.
Interpretation Of Periodic Table Symbols
Apart from the standard format of representing the elements, the symbols in the periodic table hold additional information about each element.
Understanding these symbols is crucial in gaining a deeper knowledge of the elements.
Here are the key points to interpret the periodic table symbols:
- Each symbol in the periodic table represents an element, and the position of the symbol gives information about the element’s group and period.
- The number of protons in the nucleus of an element can be determined by its atomic number, which is represented next to its symbol in the periodic table.
- The period number of an element represents the number of electron shells in the atom, while the group number indicates the number of valence electrons.
- The state of an element at room temperature is represented by its color. Metals are depicted in shades of gray, while non-metals are shown in various colors.
Understanding the symbols in the periodic table is essential in comprehending the properties and behaviors of each element.
By knowing the symbols, we can easily interpret the elemental information included in various scientific equations and communicate our knowledge with other chemistry enthusiasts.
FAQ About What Do The Symbols Mean In The Periodic Table
What Are The Symbols In The Periodic Table?
The symbols in the periodic table represent chemical elements, like h for hydrogen and o for oxygen.
What Is The Significance Of The Colors In The Key Box Of The Periodic Table?
The colors in the key box indicate different types of elements, like nonmetals, noble gases, and transition metals.
How Are The Symbols Arranged In The Periodic Table?
The symbols are arranged according to their atomic number and electron configuration.
What Is The Difference Between A Period And A Group In The Periodic Table?
A period represents the number of electron shells in an element while a group represents the number of valence electrons.
How Can I Use The Periodic Table To Predict Chemical Reactions?
The position of an element in the periodic table can give insight into its reactivity and likelihood to form compounds with other elements.
Conclusion
Understanding the symbols in the periodic table is crucial for anyone interested in science, chemistry, or even just curious about how the world works.
The symbols represent the building blocks of everything around us, from the air we breathe to the clothes we wear. The periodic table’s elements, with their distinct symbols, help us understand the composition of matter and the reactions that shape our world. These representations simplify complex scientific concepts, making them accessible and relatable. Similarly, cultural symbols hold deep meaning; for example, the Anbu symbol meaning explained in various contexts often reflects themes of secrecy, protection, and loyalty, much like the forces that bind the natural world together.
By understanding the symbols, we can understand the properties and behaviors of these elements, and how they interact with each other.
We’ve covered a lot of ground in this article, from the origins of the periodic table to the different groups and families and their respective symbols.
By paying attention to the symbols, we can unlock the secrets of the universe and better understand how everything is connected.
Whether you’re a student, a teacher, or simply someone interested in science, you can use this knowledge to your advantage and take a closer look at the world around you.






