20 Elements Names And Symbols: Complete List!
The 20 elements and their symbols are Hydrogen (H), Helium (He), Lithium (Li), Beryllium (Be), Boron (B), Carbon (C), Nitrogen (N), Oxygen (O), Fluorine (F), Neon (Ne), Sodium (Na), Magnesium (Mg), Aluminum (Al), Silicon (Si), Phosphorus (P), Sulfur (S), Chlorine (Cl), Argon (Ar), Potassium (K), and Calcium (Ca).
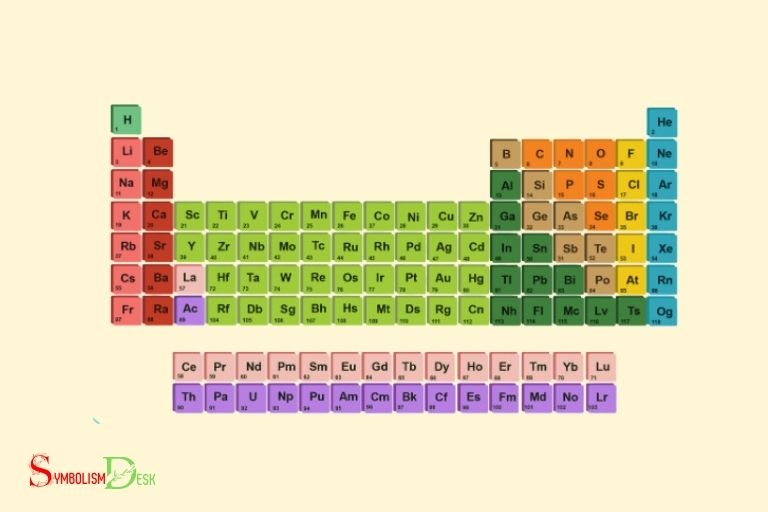
The periodic table of elements consists of 118 known elements, each represented by a chemical symbol.
The chemical symbol is a one or two-letter abbreviation for the element’s name, typically derived from the element’s Latin or Greek name. In this answer, we are providing the names and symbols for the first 20 elements in the periodic table.
The periodic table of elements is an essential tool for chemists, physicists, and other scientists to understand the properties and behaviors of elements. As elements are organized by their atomic number
List of 20 Chemical Elements with their Symbols
| Element Name | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H |
| Helium | He |
| Lithium | Li |
| Beryllium | Be |
| Boron | B |
| Carbon | C |
| Nitrogen | N |
| Oxygen | O |
| Fluorine | F |
| Neon | Ne |
| Sodium | Na |
| Magnesium | Mg |
| Aluminum | Al |
| Silicon | Si |
| Phosphorus | P |
| Sulfur | S |
| Chlorine | Cl |
| Argon | Ar |
| Potassium | K |
| Calcium | Ca |
Key Takeaway
Five Facts About 20 Chemical Elements
20 Elements Names And Symbols: An Introduction
The universe is made up of various materials that have distinct features and characteristics. In science, we refer to them as elements.
Each element has its unique name and symbol, and they are crucial in understanding the properties of different substances.
We will delve deeper into the 20 elements names and symbols, their importance, and why you should know them. Understanding the names and symbols of the 20 elements is crucial for anyone studying chemistry or working in a related field. It provides a foundation for understanding chemical reactions and the properties of different substances. Additionally, knowing the symbols of these elements is essential for reading and writing chemical equations accurately. This knowledge is also valuable in interpreting a comprehensive traffic symbol guide, especially when dealing with hazardous materials or chemical transportation. Being familiar with these symbols can help prevent accidents and ensure the safe handling of chemicals in various industries.
Understanding Elements And Their Symbols
Before we dive deep into the names and symbols of 20 elements, it’s crucial to understand what an element is and what its symbol represents. An element refers to a pure substance with the same number of protons in the nucleus of each atom.
On the other hand, a symbol represents a shorthand representation of an element’s name, typically one or two letters derived from the name.
In this section, we will explain to you the key details about elements, their symbols, and their significance.
The Importance Of Knowing The Elements
Whether you are a student in chemistry class or a professional in an industrial lab, understanding the 20 elements’ names and symbols is crucial in various ways.
Knowing the elements’ names and symbols makes it easier to communicate and record scientific data, and here are some of its crucial importance:
By knowing the 20 elements’ names and symbols we are going to discuss, you can take an important step in mastering chemistry and other scientific fields that rely on this knowledge.
The 20 Elements Names And Symbols
Now, let’s take a look at the 20 elements’ names and symbols you should familiarize yourself with.
- Hydrogen (h)
- Helium (he)
- Lithium (li)
- Beryllium (be)
- Boron (b)
- Carbon (c)
- Nitrogen (n)
- Oxygen (o)
- Fluorine (f)
- Neon (ne)
- Sodium (na)
- Magnesium (mg)
- Aluminum (al)
- Silicon (si)
- Phosphorus (p)
- Sulfur (s)
- Chlorine (cl)
- Argon (ar)
- Potassium (k)
- Calcium (ca)
Learning the elements’ names and symbols listed above will provide a solid foundation for any student or professional in the scientific field.
Knowing the 20 elements’ names and symbols is essential for anyone interested in understanding chemistry, as it forms the building blocks of all materials.
We have looked at the importance of this knowledge, explained what elements and symbols are, and listed the 20 elements’ names and symbols.
We hope that this article has helped you acquire the basic information needed for a comprehensive understanding of the elements.
The Role Of Elements In Science And Everyday Life
Elements are the building blocks of matter, and they have a significant role in both science and everyday life.
Understanding the properties and behavior of elements helps us understand the world around us, from the smallest atom to the largest stars in the universe.
Explain The Importance Of Elements In Science And Daily Life
Elements play a crucial role in science, from basic chemistry and physics to complex fields such as nuclear science and materials science.
The study of elements and their properties has led to numerous innovations and technological advancements that have transformed our lives, including:
- Development of new medicines and drugs
- Development of new materials for industrial application
- Production of clean energy
- Advancements in space exploration
- Development of electronic devices
In our daily life, we use numerous household items that are made up of different elements, for example, oxygen in the air, iron in cookware, hydrogen in water, and carbon in food.
Provide Examples Of Common Household Items And Their Element Composition
- Air: Oxygen (o) – 20.95%, nitrogen (n) – 78.09%, argon (ar) – 0.93%
- Water: Hydrogen (h) and oxygen (o) – h2o
- Food: Carbon (c), hydrogen (h), and oxygen (o)
- Salt: Sodium (na) and chlorine (cl) – nacl
- Sugar: Carbon (c), hydrogen (h), and oxygen (o)
- Doorknob: Brass – copper (cu) and zinc (zn)
- Iron skillet: Iron (fe)
- Aluminum foil: Aluminum (al)
- Gold jewelry: Gold (au)
- Stainless steel utensils: Iron (fe), chromium (cr), and nickel (ni)
Discuss The Significance Of Studying Elements And Their Symbols
Studying elements and their symbols is essential for scientists and students of science. It allows scientists to categorize elements, predict properties and reactions, and create new materials.
The symbols used for each element are vital as they make it easy to represent and differentiate between the numerous elements.
Symbols are used by scientists all over the world and provide a common language for scientific communication.
Elements and their symbols play a crucial role in both science and everyday life. They make up the matter around us, and by studying them, we can understand the world better.
The History Of Elements And Symbols
The study of elements and symbols dates back to ancient times when people explored minerals and rocks. Here are some highlights of the early developments in the discovery of elements and symbols:
- The ancient greeks were the first to theorize about the composition of matter, proposing the concept of the atom.
- The first scientific classification of elements began in the 16th century with the works of georg agricola. He is considered the “father of mineralogy.”
- In the late 18th century, antoine lavoisier developed the first comprehensive list of elements.
- An early version of the periodic table was proposed in 1862 by alexandre-emile béguyer de chancourtois, who arranged elements by increasing atomic weight around a cylinder.
The contributions of various scientists have shaped the way we categorize elements and symbols today.
Here are some of the key contributors and their contributions:
- Dmitri mendeleev is credited with the development of the modern periodic table. He arranged elements by atomic weight and left spaces for unknown elements, which were later discovered and filled the gaps.
- Marie curie discovered two radioactive elements- radium and polonium.
- Glenn t. seaborg discovered twelve new elements, including plutonium and americium. He also proposed the concept of the actinide series.
Over time, the periodic table has evolved to reflect new discoveries and changes in scientific understanding.
Here are some of the major developments:
- In the 20th century, the arrangement of elements was based on atomic number, rather than atomic weight.
- New elements continue to be discovered and added to the periodic table. In 2015, four new elements were officially recognized and named.
- Scientists continue to work on refining the periodic table, with new proposals for reorganizing elements based on electronic configurations and different variations.
The periodic table remains a foundational tool in the study of chemistry and has been a key factor in the discovery and understanding of elements and symbols.
20 Elements Names And Symbols
Introduce The 20 Elements And Their Symbols
The periodic table of elements contains a total of 118 elements; each element has its unique chemical symbol.
We will focus on the 20 elements that are commonly found on earth. These elements have diverse physical and chemical properties that are used in everyday life.
Provide A Brief Overview Of Each Element And Their Properties
- Hydrogen (h): The lightest element on the periodic table, it is the most abundant element in the universe. It has a vast range of industrial applications, from producing ammonia for fertilizers to being used as a fuel for rockets.
- Helium (he): Helium is the second lightest element in the universe. It is known for its ability to make things float, and it is often used to fill balloons. It’s also used in medical applications, such as mri machines and as a cooling agent for nuclear reactors.
- Carbon (c): Carbon is known as the building block of life. It is present in all living organisms and is essential for organic chemistry processes. It is also used in manufacturing materials like steel, diamonds, and graphite.
- Nitrogen (n): Nitrogen is an essential component in the atmosphere. It is used in the production of fertilizers, in fire suppression systems, and in the manufacturing of electronic components.
- Oxygen (o): Oxygen is the element essential for sustaining life. It is used in the manufacture of medicines, rocket fuel, and steel production.
- Fluorine (f): Fluorine is used in chemical processes to create refrigerants, including air conditioning and freezers. It is also used in the production of toothpaste and water treatment.
- Sodium (na): Sodium is an essential nutrient for the human body. It is also used in the manufacturing of glass, soaps, and other cleaning products.
- Magnesium (mg): Magnesium is used in the creation of lightweight alloys for manufacturing. It is also an essential component for healthy bone development and maintenance.
- Aluminum (al): Aluminum is the third most common element found on earth. It is used in the production of a vast range of products, from aircraft frames to packaging materials.
- Silicon (si): Silicon is the primary component in computer microprocessors. It is also used in solar panels, glass production, and semiconductors.
- Phosphorus (p): Phosphorus is used in the manufacture of fertilizers, detergents, and steel production.
- Sulfur (s): Sulfur is used in the manufacturing industry to produce sulfuric acid, one of the most widely used industrial chemicals.
- Chlorine (cl): Chlorine is used in water treatment to kill bacteria. It is also used in the manufacturing of plastics, pharmaceuticals, and pesticides.
- Potassium (k): Potassium is an essential nutrient for the human body. It is also used in the manufacturing of fertilizers and gunpowder.
- Calcium (ca): Calcium is an essential component for healthy bone development and maintenance. It is also used in the manufacturing of cement and steel.
- Iron (fe): Iron is the most common element found on earth. It is used in steel production, and it is an essential nutrient for the human body.
- Copper (cu): Copper is used in electrical wiring, plumbing, and the manufacturing of cookware and coins.
- Zinc (zn): Zinc is used in the manufacturing of alloys such as brass and in galvanizing iron and steel.
- Iodine (i): Iodine is used in the manufacturing of antiseptics, dyes, and x-ray contrast agents.
- Gold (au): Gold is a valuable metal used in jewelry, electronics, and currency.
Explain Why These 20 Elements Were Selected
These 20 elements were chosen for their commonality and importance in everyday life. They are essential components in various industries and are used in various products that we use daily.
Understanding these elements and their uses is crucial for appreciating their importance and impact on our lives.
The First 10 Elements
List The First 10 Elements And Their Symbols
The first 10 elements in the periodic table are important building blocks of our world.
Below are their symbols along with a brief description of each element:
- Hydrogen (h): The simplest element, mostly found in water and fuels, used in the production of ammonia, and as rocket fuel.
- Helium (he): A non-toxic, odorless, and colorless noble gas used in cryogenics, welding, and as a lighter-than-air gas.
- Lithium (li): A soft, silvery-white chemical element, used in batteries, ceramics, and the treatment of bipolar disorder.
- Beryllium (be): A hard, gray metal, used in nuclear reactors, missiles, and satellites due to its strength and lightness.
- Boron (b): A metalloid element mostly used in the production of heat-resistant glass, detergents, and insecticides.
- Carbon (c): The basis of all known life on earth, used for making diamonds, steel, and in various forms in the field of nanotechnology.
- Nitrogen (n): The most abundant element in earth’s atmosphere, used in fertilizer, the making of ammonia, and liquid nitrogen.
- Oxygen (o): The second most abundant element in the universe, necessary for supporting life on earth, used in the production of steel and in medical treatments.
- Fluorine (f): A pale-yellow gas, used in toothpaste, refrigerants, and the making of uranium hexafluoride.
- Neon (ne): A noble gas, used in neon signs, laser technology, and cryogenics.
Importance Of The First 10 Elements
Each of the first 10 elements plays an important role in our daily lives.
Below are some key points to better understand their significance:
- Hydrogen: Used to power rockets and fuel cells, but also plays a crucial role in many biological reactions through its bonds in water molecules.
- Helium: Used to cool mri machines and nuclear reactors. It is also used in blimps and balloons as a lifting gas.
- Lithium: Used to treat bipolar disorder and as an important component in batteries for mobile phones and laptops.
- Beryllium: Lightweight but strong, used in nuclear and aerospace industries for its unique combination of properties.
- Boron: Used to make boric acid, a compound that has numerous applications in industry and medicine. Boron is used to create heat-resistant glass, detergents, and fertilizers.
- Carbon: An essential element for life and used to create materials such as diamond, graphene, and nanotubes, which have unique electrical and mechanical properties.
- Nitrogen: Essential for plant growth, used in the production of fertilizers, and in the manufacturing of ammonia, which is used in many industrial processes.
- Oxygen: Essential for human life and used in the production of steel and various chemicals. Oxygen is also used in the medical industry to help people breathe.
- Fluorine: Used in toothpaste, refrigerants, and in the processing of uranium. Fluorine is also used in many industrial processes, including the production of materials such as plastics and textiles.
- Neon: Used in neon lights, lasers, and in cryogenic cooling. Neon is also used in vacuum tubes, as a refrigerant gas, and in geological dating.
Each element has a significance that is not only practical but also essential in many aspects of our daily life. Knowing their properties and applications can help us understand how they contribute to our world and bring value to our lives.
The Second 10 Elements
Moving on from the first ten elements, we will now focus on the next ten. Each element in the periodic table has its importance in various fields, and understanding their characteristics is crucial in improving our lives and the world around us.
In this section, we will discuss the second ten elements and their symbols.
List The Second 10 Elements And Their Symbols
Here is a list of the second ten elements and their corresponding symbols:
- Sodium (na)
- Magnesium (mg)
- Aluminum (al)
- Silicon (si)
- Phosphorus (p)
- Sulfur (s)
- Chlorine (cl)
- Argon (ar)
- Potassium (k)
- Calcium (ca)
Provide A Brief Description Of Each Element
- Sodium (na): This soft metal is highly reactive in air and water and is essential for human life. Sodium is used in the production of soap, paper, and as a coolant in nuclear reactors.
- Magnesium (mg): A light metal that is essential for plant and animal life. Magnesium is used in alloys for airplanes, cars, and medical implants.
- Aluminum (al): A versatile metal that is lightweight, strong, and resists corrosion. It is used in construction, transportation, and packaging.
- Silicon (si): An abundant and essential element used in the production of semiconductors and computer chips.
- Phosphorus (p): A non-metallic element found in nature in phosphate minerals. Phosphorus is used in fertilizers, detergents, and matches.
- Sulfur (s): A non-metal used in the production of sulfuric acid and fertilizers. It is a key component in gunpowder and matches.
- Chlorine (cl): A highly reactive non-metal used to disinfect water and as a bleaching agent in paper production.
- Argon (ar): An inert gas used in welding and as an insulating gas in windows and light bulbs.
- Potassium (k): An essential nutrient for plant and animal life. Potassium is used in fertilizers and to make soap and glass.
- Calcium (ca): A vital element for strong bones and teeth. Calcium is used in the production of cement, cheese, and paper.
Explain Their Importance
Each element has its importance in various fields. From building strong bones to producing semiconductors, each element plays a crucial role in our daily lives.
The second ten elements have their unique properties that make them useful in diverse industries, including construction, transportation, medicine, and technology.
Understanding the characteristics of each element and their importance can lead to innovations in various fields and improve the quality of life for humans.
Using Elements And Symbols In Science
Chemical elements are substances that cannot be broken down into smaller parts or simpler substances by chemical means.
Elements are the basic blocks of matter, and they are essential to our understanding of different scientific phenomena.
Scientists often distinguish elements from one another using symbols, which consist of one or two letters derived from the element’s name.
In this section, we will discuss how elements and symbols are used in scientific research.
Discuss How Elements And Symbols Are Used In Scientific Research
The use of elements and symbols is essential in scientific research. Scientists use symbols to represent elements, which makes it easier for them to communicate their findings.
Here are some ways elements and symbols are used in scientific research:
- Identifying elements: Symbolic representation of elements helps in identifying elements in various substances. Scientists use the symbols to represent elements and look for them in substances they are analyzing. For instance, the symbol h represents hydrogen, and scientists use this symbol to identify hydrogen in various substances.
- Describing chemical reactions: Elements and symbols help in describing chemical reactions accurately. A chemical equation uses symbols to describe a chemical reaction. For example, the chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to form water is represented as follows: 2h₂ + o₂ → 2h₂o.
- Creating new materials: Scientists use elements to create new materials that may be useful in various industries. For example, the element carbon is used to make diamonds, pencils, and various other materials.
- Understanding the basis of life: Elements and symbols play a crucial role in understanding the basis of life. The human body is made up of many elements, including carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen.
Provide Examples Of Studies That Utilize These 20 Elements
Numerous studies have used different elements, and some of the most common elements used in scientific research include hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur, among others.
For instance:
- Nitrogen has been used in studying the effects of climate change on ecosystems, particularly in aquatic ecosystems. Researchers have shown that nitrogen deposition can significantly impact plant growth.
- Carbon has been used in the research of climate change, particularly in the context of greenhouse gases. Carbon dioxide, in particular, is a significant contributor to global warming.
- Hydrogen has been used in fuel cell research, which aims to create clean energy. Hydrogen fuel cells produce electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen.
Explain The Significance Of Understanding These Elements In Science
Understanding the different chemical elements is paramount to any scientific endeavor. In science, various phenomena can be explained by understanding the composition of substances at a molecular or atomic level.
For instance:
- Medical research: In medical research, understanding elements helps in finding new treatments for various diseases. For example, carbon is essential in creating new medications as it forms the backbone for most organic molecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates.
- Climate change mitigation: Understanding how different elements contribute to climate change can help in finding solutions. Carbon, for instance, can be sequestered to prevent it from entering the atmosphere, thus reducing the rate of global warming.
- Exploring space: Understanding the different chemical elements helps scientists in exploring space. Detecting elements in other planets and stars helps in understanding their composition and origins.
Understanding elements and symbols is vital in scientific research. Elements are the building blocks of matter and help in explaining a wide range of phenomena.
Symbols, on the other hand, help in describing elements and their properties, making it easier for scientists to communicate their findings.
Are There Any Additional Names and Symbols of Elements Beyond the 20 Listed?
Yes, there are indeed additional elements’ names and symbols beyond the 20 that are commonly listed. These additional elements, such as einsteinium (Es) or lawrencium (Lr), can be found towards the end of the periodic table. Each element has its own unique symbol and name, helping to identify and categorize them in the world of chemistry.
FAQ Of 20 Elements Names And Symbols
What Are The First 10 Elements Names And Symbols?
The first 10 elements in the periodic table with their symbols are:
1. Hydrogen – h
2. Helium – he
3. Lithium – li
4. Beryllium – be
5. Boron – b
6. Carbon – c
7. Nitrogen – n
8. Oxygen – o
9. Fluorine – f
10. Neon – ne
What Are The Last 10 Elements Names And Symbols?
The last 10 elements in the periodic table with their symbols are:
109. Meitnerium – mt
110. Darmstadtium – ds
111. Roentgenium – rg
112. Copernicium – cn
113. Nihonium – nh
114. Flerovium – fl
115. Moscovium – mc
116. Livermorium – lv
117. Tennessine – ts
118. Oganesson – og
What Are The Most Common Element Names And Symbols?
Some of the most common elements and their symbols, in no particular order, are:
1. Nitrogen – n
2. Oxygen – o
3. Hydrogen – h
4. Carbon – c
5. Calcium – ca
6. Iron – fe
7. Gold – au
8. Silver – ag
9. Aluminum – al
10. Copper – cu
What Do The Letters In The Element Symbols Stand For?
The letters in the element symbols typically stand for the first letter or two of the element’s name. For example, h stands for hydrogen and o stands for oxygen. However, some symbols may come from different languages or have historical meanings.
What Are The Smallest And Largest Elements In The Periodic Table?
The smallest element in the periodic table is hydrogen, with one proton and one electron. The largest element is oganesson, with 118 protons and 176 neutrons.
Conclusion
With that, we have come to the end of our discussion on the 20 elements and their symbols. These elements form the building blocks of our world, allowing matter to exist in different forms.
By understanding their properties, we are able to manipulate them in ways that have revolutionized our lives.
From the common elements like hydrogen and oxygen that make up the air we breathe and the water we drink, to the more exotic elements like platinum and gold, the periodic table is a testament to the complexity and wonder of the natural world.
By keeping track of these elements and their symbols, you can expand your knowledge and understanding of the world around you, and possibly even discover new ways to use them for the betterment of humanity.
In the end, the periodic table is more than just a chart, it is the key to unlocking the mysteries of the universe.






