118 Element Name And Symbol: Complete List!
There are 118 known chemical elements, each with their unique name and symbol.
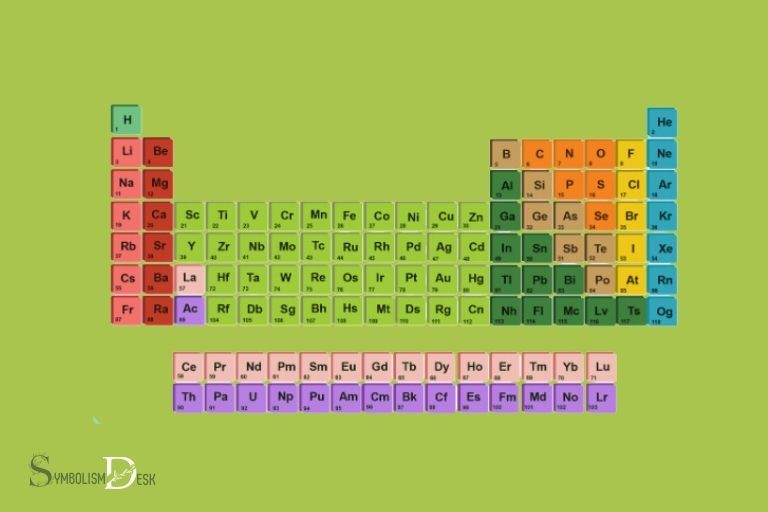
The periodic table of elements organizes these 118 chemical elements based on their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties.
Elements are represented by their symbol, which consists of one or two letters derived from their Latin, Greek, or English name.
The periodic table helps scientists and chemists understand the relationships between the elements and predict their properties.
It is organized into periods (rows) and groups (columns) based on similar properties, such as reactivity and electron configuration.
By understanding the periodic trends, one can make better predictions about the chemical behavior of a specific element and its potential applications in various industries.
Element 118 – Name and Symbol
| Element | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H |
| Helium | He |
| Lithium | Li |
| Beryllium | Be |
| Boron | B |
| Carbon | C |
| Nitrogen | N |
| Oxygen | O |
| Fluorine | F |
| Neon | Ne |
| Sodium | Na |
| Magnesium | Mg |
| Aluminum | Al |
| Silicon | Si |
| Phosphorus | P |
| Sulfur | S |
| Chlorine | Cl |
| Argon | Ar |
| Potassium | K |
| Calcium | Ca |
| Scandium | Sc |
| Titanium | Ti |
| Vanadium | V |
| Chromium | Cr |
| Manganese | Mn |
| Iron | Fe |
| Cobalt | Co |
| Nickel | Ni |
| Copper | Cu |
| Zinc | Zn |
| Gallium | Ga |
| Germanium | Ge |
| Arsenic | As |
| Selenium | Se |
| Bromine | Br |
| Krypton | Kr |
| Rubidium | Rb |
| Strontium | Sr |
| Yttrium | Y |
| Zirconium | Zr |
| Niobium | Nb |
| Molybdenum | Mo |
| Technetium | Tc |
| Ruthenium | Ru |
| Rhodium | Rh |
| Palladium | Pd |
| Silver | Ag |
| Cadmium | Cd |
| Indium | In |
| Tin | Sn |
| Antimony | Sb |
| Tellurium | Te |
| Iodine | I |
| Xenon | Xe |
| Cesium | Cs |
| Barium | Ba |
| Lanthanum | La |
| Cerium | Ce |
| Praseodymium | Pr |
| Neodymium | Nd |
| Promethium | Pm |
| Samarium | Sm |
| Europium | Eu |
| Gadolinium | Gd |
| Terbium | Tb |
| Dysprosium | Dy |
| Holmium | Ho |
| Erbium | Er |
| Thulium | Tm |
| Ytterbium | Yb |
| Lutetium | Lu |
| Hafnium | Hf |
| Tantalum | Ta |
| Tungsten | W |
| Rhenium | Re |
| Osmium | Os |
| Iridium | Ir |
| Platinum | Pt |
| Gold | Au |
| Mercury | Hg |
| Thallium | Tl |
| Lead | Pb |
| Bismuth | Bi |
| Polonium | Po |
| Astatine | At |
| Radon | Rn |
| Francium | Fr |
| Radium | Ra |
| Actinium | Ac |
| Thorium | Th |
| Protactinium | Pa |
| Uranium | U |
| Neptunium | Np |
| Plutonium | Pu |
| Americium | Am |
| Curium | Cm |
| Berkelium | Bk |
| Californium | Cf |
| Einsteinium | Es |
| Fermium | Fm |
| Mendelevium | Md |
| Nobelium | No |
| Lawrencium | Lr |
| Rutherfordium | Rf |
| Dubnium | Db |
| Seaborgium | Sg |
| Bohrium | Bh |
| Hassium | Hs |
| Meitnerium | Mt |
| Darmstadtium | Ds |
| Roentgenium | Rg |
| Copernicium | Cn |
| Nihonium | Nh |
| Flerovium | Fl |
| Moscovium | Mc |
| Livermorium | Lv |
| Tennessine | Ts |
| Oganesson | Og |
Key Takeaway
Five Facts About 118 Element Name And Symbol
Introducing 118 Element Name And Symbol
Brief History Of Elements And Why They Are Essential To Science
Elements are the basic building blocks of nature. They were first identified by ancient scientists and philosophers, who classified them based on their properties.
The concept of elements has been used in many fields such as chemistry, physics, and astronomy, and it has played an essential role in the development of modern science.
List Of 118 Elements And Their Symbols, Including The Newly Synthesized Ones
The periodic table of elements contains 118 elements, arranged in order of increasing atomic number. Each element has a unique symbol and a name that reflects its properties. Elements are divided into categories based on their properties, such as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. The periodic table has been a key tool for chemists and scientists to understand the behavior and properties of different elements. By using the periodic table, researchers can discover complete element symbols, atomic masses, and electron configurations for each element, allowing for a deeper understanding of the fundamental building blocks of matter.
Importance Of Element Names And Symbols In Science And Industry
Element names and symbols play a crucial role in science and industry. They provide a common language that scientists and engineers can use to communicate ideas and data.
Some important reasons why names and symbols are essential include:
Elements play an essential role in science as the basic building blocks of nature. The list of 118 elements is an incredible achievement, allowing scientists to better understand our world and make significant advances in science and industry.
The use of names and symbols of elements provides a universal language that is important for communication between scientists and the public.
The Significance Of Element Names And Symbols
Every element in the periodic table has a unique name and symbol, which allows us to study and identify their properties.
The name and symbol of an element play a significant role in its identification and classification, and their origins can often reveal interesting stories and facts.
In this section, we will discuss how element names and symbols are determined, the patterns and commonalities in element names and symbols, and examples of how element symbols are used in practical applications.
How Element Names And Symbols Are Determined
The process of determining an element’s name and symbol is not arbitrary but follows a set of guidelines and rules established by the international union of pure and applied chemistry (iupac).
These guidelines ensure that the name and symbol of the new element reflect its properties or discoveries and have international acceptance.
Some of the factors taken into account during the naming process include the element’s discoverer, its properties, its place of discovery, and its historical significance.
Once an element is discovered and confirmed, its name and symbol are proposed and reviewed by the iupac for approval.
The Patterns And Commonalities In Element Names And Symbols
While each element has a unique name and symbol, some patterns and commonalities can be found in their naming conventions.
For example, elements in the same group or family often share similar properties and have names that end in the same suffix or prefix.
Elements named after famous scientists or places with scientific significance often have symbols that reflect their namesake.
For example, einsteinium has the symbol es to honor physicist albert einstein, while californium has the symbol cf to pay homage to the state of california, where it was first synthesized.
Examples Of How Element Symbols Are Used In Practical Applications
Element symbols are used in several applications, such as chemistry, physics, and engineering. They are used to represent elements in formulas, equations, and reactions, making it easier for scientists to communicate and share their findings.
In chemical compounds, the elemental symbols are used to denote the composition of the compound, indicating which elements and how many atoms of each element are present in the compound.
This makes it easier to identify and study the properties and behavior of the compound.
In nuclear physics, element symbols help distinguish between different isotopes of the same element. Isotopes have the same atomic number but a different number of neutrons, making them have different masses.
The element symbol followed by the atomic mass number and the atomic number is used to represent isotopes, such as carbon-14 or uranium-235.
Element names and symbols are crucial for our understanding and study of the world around us. They represent the unique properties and discoveries of elements and are used in various fields to communicate ideas and information.
Understanding The Periodic Table
Overview Of The Periodic Table And Its Evolution Over Time
The periodic table is the cornerstone of chemistry. It is a graphical representation of all the known chemical elements and their properties.
Russian chemist dmitri mendeleev is credited with creating the first recognizable periodic table in 1869. The periodic table has undergone a few changes since its inception.
Here are some of the key takeaways regarding the periodic table:
- The periodic table is organized in rows and columns.
- The rows, called periods, are arranged according to the number of electrons in their outermost shells.
- The columns, called groups, organize elements with similar properties.
- The periodic table’s modern form is based on the periodic law, which states that the elements’ properties are periodic functions of their atomic number.
How Elements Are Organized On The Periodic Table
The periodic table’s organization is intricate, with each element’s properties reflected in its placement.
Here are the basics on how elements are arranged in the periodic table:
- Elements in the same row share the same number of electron shells.
- The elements in each column share similar physical and chemical properties.
- The closer two elements are on the periodic table, the more alike they are in terms of chemical behavior.
- Elements in the far left column, like hydrogen and lithium, are highly reactive metals. On the other hand, elements like neon and helium are nonreactive.
Explanation Of The Color-Coding And Numbering System Used On The Periodic Table
The periodic table also uses a color-coding and numbering system to make categorization simple.
Here’s how this system works:
- Each element on the periodic table has a unique atomic number that identifies its element type.
- The colors on the periodic table are used to differentiate between the different element blocks, which are s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block.
- The atomic number is located above each element, and the chemical symbol below it.
- The elements’ atomic masses are listed beneath their symbols.
That’s a brief overview of the essentials of the periodic table – it’s an intricate yet vital component of chemistry that has evolved significantly over time.
A Closer Look At Selected Elements
From aluminum to zinc, there are 118 known elements that make up everything around us. Some of them are commonly used in everyday life and a few have extraordinary properties that can be utilized in various industries and applications.
In this section, we’ll take a closer look at some of these elements and explore why they matter.
Noteworthy Properties Of Some Of The Elements And Why They Are Important
- Carbon: With six protons and six neutrons, carbon is the element of life. It has the unique ability to bond with other elements to create essential organic compounds, such as proteins and dna. Carbon also conducts electricity and is used in electronics, including smartphones and computers.
- Gold: Gold has been valued for centuries for its rarity and beauty. Its unique properties, including malleability, ductility, and conductivity, make it essential in various industries such as electronics, jewelry, and dentistry. Gold nanoparticles also have the potential for use in cancer therapy.
- Hydrogen: Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. It is highly flammable and has a low atomic weight, making it an excellent fuel source for rockets and other space vehicles. Hydrogen is also used in the production of ammonia, which is essential in the manufacturing of fertilizers.
Descriptions Of How These Elements Are Used In Various Industries And Applications
- Silicon: Silicon is used in electronics as a semiconductor and has revolutionized the computer industry. It’s also present in various solar panels, which convert light into energy.
- Iron: Iron is an essential element in the human body, but it is also used in building and construction due to its strength and durability. It is commonly used in bridges, buildings, and other infrastructure projects.
- Calcium: Calcium is necessary for strong bones and teeth, but it is also used in the production of cement, which is an essential component of modern construction.
The Role Of These Elements In Everyday Life And Why They Matter
- Oxygen: Oxygen is essential for all living organisms and is a critical component of the earth’s atmosphere. It’s also used to support combustion in various industries and for medical purposes.
- Nitrogen: Nitrogen makes up 78% of the earth’s atmosphere and is essential for plant growth. It’s also used in the production of fertilizers and in the food industry to preserve freshness.
- Sodium: Sodium is essential for maintaining proper fluid balance in the body and is a key component of table salt. It’s also used in various industrial processes, including the manufacturing of soaps and detergents.
As we can see, the elements that make up everything around us are incredibly diverse and have unique properties.
By understanding their importance in various industries and their role in everyday life, we can appreciate just how essential they are to our world.
Is There a Complete List of Traffic Symbols with Names?
Finding a comprehensive list of traffic symbols with names can be useful for both drivers and pedestrians. Knowing their meanings promotes road safety and understanding. Such a list provides information about various signs like stop signs, yield signs, speed limit signs, and more. Familiarizing oneself with traffic symbols with names promotes responsible commuting and aids in preventing accidents.
FAQ On 118 Element Name And Symbol
What Are The First 20 Element Names And Symbols?
The first 20 elements and their symbols are hydrogen (h), helium (he), lithium (li), beryllium (be), boron (b), carbon (c), nitrogen (n), oxygen (o), fluorine (f), neon (ne), sodium (na), magnesium (mg), aluminum (al), silicon (si), phosphorus (p), sulfur (s), chlorine (cl), argon (ar), potassium (k), and calcium (ca).
What Is The Difference Between Element Name And Symbol?
An element name is a word or pair of words that give a substance a particular identity, while an element symbol is a one- or two-letter abbreviation used to identify an element.
How Many Elements Have Names Based On Countries?
There are four elements named after countries – francium (fr) named after france, polonium (po) named after poland, germanium (ge) named after germany, and americium (am) named after the united states.
Why Are Some Element Symbols Different From Their Names?
Some element symbols are different from their names to avoid confusion between different elements with similar names. For example, iodine is assigned the symbol i, because the symbol i has already been used for the element helium.
Who Named The Elements?
The elements have been named by a variety of people, including the element discoverer, scientists who contributed to the study of the element, places, and even mythological figures.
Conclusion
From the above-discussed blog post, it is clear that elements play a significant role in our daily lives.
While some elements such as oxygen and carbon are essential for survival, others like gold and silver have great economic value due to their rarity.
Memorizing the 118 element names and symbols can be overwhelming for many, but it should not be.
Instead, learners can make use of the periodic table, which organizes all elements systematically, making it easier to navigate through them.
Though their names and symbols may look confusing at first glance, understanding and familiarizing oneself with them can help learners appreciate the properties and uses of elements.
The periodic table and the 118 elements should be celebrated for their contribution to life and science.






